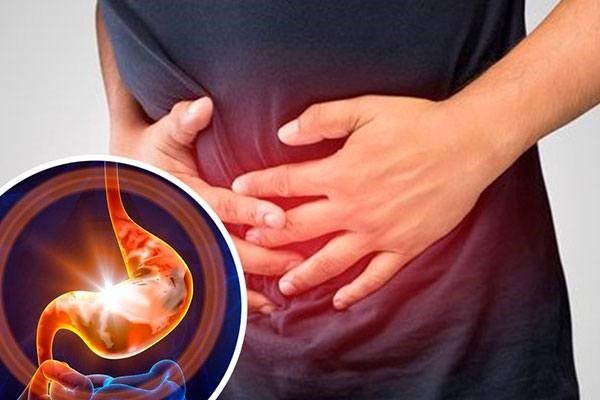
Gastritis
Gastritis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the lining of the stomach. This inflammation can result from various factors, including infection with Helicobacter pylori bacteria, excessive alcohol consumption, prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin or ibuprofen, stress, autoimmune diseases, or bile reflux. Gastritis can be acute, with sudden onset and short duration, or chronic, persisting over an extended period.
Symptoms of gastritis can vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of inflammation but may include abdominal pain or discomfort, nausea, vomiting, bloating, loss of appetite, and a feeling of fullness after eating small amounts. In severe cases or with prolonged inflammation, gastritis can lead to complications such as peptic ulcers, gastrointestinal bleeding, or an increased risk of stomach cancer, particularly in individuals with chronic gastritis caused by H. pylori infection.
Diagnosis of gastritis typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as blood tests to check for H. pylori antibodies, stool tests for signs of infection or bleeding, upper endoscopy (esophagogastroduodenoscopy) with biopsy to visualize the stomach lining and obtain tissue samples for analysis, and imaging studies such as an upper gastrointestinal series or abdominal ultrasound to evaluate the extent of inflammation or complications.
Treatment for gastritis aims to alleviate symptoms, reduce inflammation, and address underlying causes. This may involve lifestyle modifications such as avoiding alcohol, spicy or acidic foods, quitting smoking, managing stress, and reducing NSAID use. Medications such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) to decrease stomach acid production, H2 receptor antagonists to reduce acid secretion, antacids for symptom relief, antibiotics for H. pylori eradication, or medications to protect the stomach lining may be prescribed based on the specific cause and severity of gastritis. In chronic cases or with complications, regular monitoring and follow-up with healthcare providers are essential to prevent complications and ensure optimal management of gastritis.
Book Appointment
.jpg)
.jpg)

